Blockchain Demo
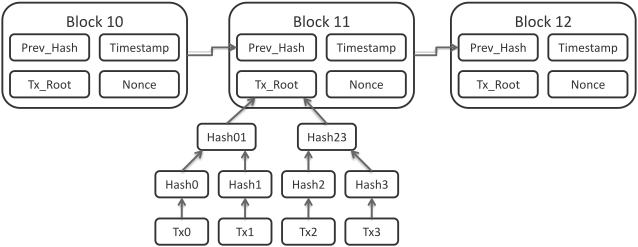
A blockchain is a ledger in which each entry contains a unique fingerprint - the hash - of the previous entry. This hash also affects the next block's own hash, which is included in the block after that, and so on, ensuring that any change to an early block can easily be detected.
How To Use This Page
Every row represents a single block in the blockchain. Changing the transactions in a block and pressing "Update Block" will generate a new hash for that block, using its generation, previous hash and transactions.
Because the new hash does not match the subsequent block's copy of that block's hash, it is flagged as being invalid.
By copying the hash to the next block and re-hashing that block, it is possible to generate a new valid blockchain.
Generation
Previous Hash
Transactions
New Hash
Somebody trying to add, remove or modify a transaction from an old block must generate a new hash not just for that block, but also every subsequent block.
As long as the hashing process is not trivial, such a forgery becomes increasingly difficult as the blockchain grows.